
In this blog post we will consider that you are already running around 10,000 campaigns across 5 different channels and you know which of these are running well and producing a lot of profit and which of these are running poor. At every beginning of the month you have to assign 100,000 € to the best running campaigns to get the most revenue.
In other words:
How to get the biggest bang for your marketing bucks.
In an earlier blog post we discussed a strategy how you can find with an optimal strategy the one marketing channel that will give you the most revenue. We considered the finding as a multi-armed-bandit-problem and showed that a sophisticated strategy like the incentergy one can save your up to 6% of you marketing budget.
Marginal Utility
The good news is you already know which of these 10,000 campaigns performs best. You now might ask why we do not just allocate our 100,000 € to the best performing campaign and skip the other 9,999. The reason for this is:
decreasing marginal utility
This means that the CPO (Costs-Per-Order) for your first orders in a certain marketing campaign are a lot cheaper then for later campaign.
The following illustration shows this:
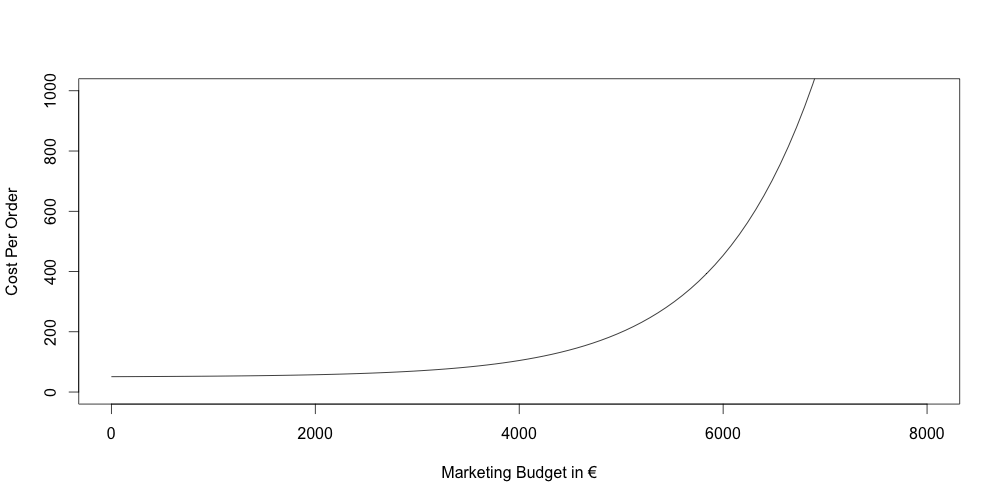
As you can see at the beginning we pay around 50 € to get one order. This works well for the first 40 orders but when we are spending more then 2000 € we are already paying 57 € to get another order. From 4000 € we are already paying 104 € to get another order. This goes on and on. So it might be the case that after paying 2000 € in this campaign there is another campaign where it is cheaper to buy another order.
Let me explain this problem with an easy example.
The buffet problem
Imagine you are in a hotel at the cake buffet and there are 5 kinds of dishes:
- Cream cake
- Fruits
- Apple pie
- Cheese cake
- Brownies
Creamcake is your favourite cake but nevertheless you are not only taking creamcake you are also eating from the other options. This is called marginal utility. The third piece of cream cake is not as good as the first brownie.
The graph below shows the different utility functions of the different options:
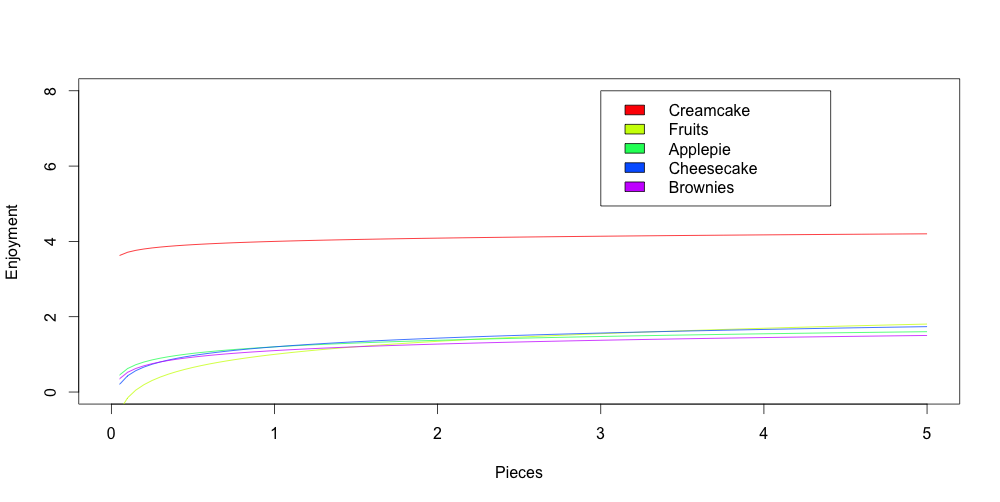
As you can see the first piece of Creamcake is very good but the second does not increase your enjoyment that much. Compared to fruits which are not that good at all but you can eat a lot of them and will still get some enjoyment.
The question is now, you are allowed to eat 10 pieces from the buffet what would be the maximal enjoyment that you could get?
This process is called optimization. In our case it is a non linear optimization with constraints. The incentergy platform can optimize such problems and give you the perfect solution.
For the buffet problem the best solution for 10 pieces is as follows:
- 0.847 pieces of cream cake
- 3.436 pieces of fruits
- 1.713 pieces of apple pie
- 2.289 pieces of cheese cake
- 1.713 pieces of brownies

Leave a Reply